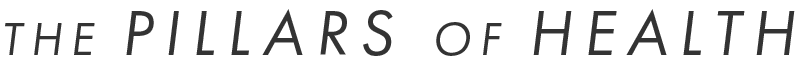Mold isn’t magic. Yes it’s often hidden from plain view, but it isn’t entirely undetectable — and it’s certainly not a mystery.
What causes mold, how it thrives, and what it can do to humans; we can understand these things.
Yet if we, as people, are unaware of how mold works, it can become almost like a dark magic: invisible, mysterious and dangerous.
Let’s bring mold into the light.
Above all, the absolute best weapons against mold are awareness and knowledge.
Take time to gather facts, develop a strategy, and be equipped to handle any situation.
Mold has a job in nature — as a fungus — to break down dead matter.
Of course, nature is full of decaying things! And fungus quickly decomposes them, turning dead matter into healthy, rich soil.
Unfortunately, the buildings we live in are made using lots of dead matter, ripe to be decomposed by mold.
This means our buildings are essentially food for mold. Mold spores are everywhere — and all it takes is a little water for a spore to sprout.
“Mold growth begins when a single spore of fungus lands on an organic surface. This includes all biodegradable materials, ranging from paper to leather.“
Sciencing.com
Moisture + Food
Mold needs two things: Moisture and food.
Any biodegradable material is a ready source of food for mold. Buildings are full of extremely-processed, biodegradable materials.
In fact, dust is great mold food.
Mold Spreads
Mold spreads by releasing millions of microscopic spores.
When a spore finds moisture, it will sprout quickly.
Mycotoxins
Mold also produces “mycotoxins” as a defense mechanism — which can harm the nervous system, hormones, and the gut, and activate the immune system.
Humidity Feeds Mold
Leaks aren’t the only source of moisture that encourages mold growth.
When humidity rises above 50-60%, spores start sprouting.
“As the mold absorbs moisture in the air, it swells in size to form a thin thread known as a hyphae. The hyphae quickly spread and extend across the surface, assuming conditions are sufficient for growth.”
SCIENCING.COM
Mold Spores Are Everywhere In Nature
Nature is abundant with dead and decaying matter. Microbe-rich soils are a feeding ground.
Every time the door or a window opens, fungal spores fly in a building.
So what makes mold such a problem inside buildings?
“There’s never been a mold test that we’ve done that didn’t have any mold. Every house, every environment has mold spores.
It becomes an issue when the concentration of mold spores in a home is greater than what is found outside.”

Mold is a robust, hardy organism.
Mold Can Sprout Fast
Spores can sprout almost immediately from the time moisture appears on a surface.
Mold growths, or colonies, can begin to grow on a damp surface within 24 to 48 hours.
fema.gov
Dead Mold Is Still Harmful
Do Not Disturb
Dead mold is full of spores which are very much still alive.
When dead mold is disturbed, millions of spores and mycotoxins are released into the air.
Spores can survive indefinitely. Therefore, long-dead mold can very easily become living mold.
As Mold Dries Out…
As humidity falls, mold ramps up spore production to increase the survivability of the species.
Spore counts can easily escalate up to 10X normal numbers after turning on a dehumidifier.

This is a survival mechanism for the mold. Increased spore production means the species will better survive a temporary lack of moisture.
Increased spore counts can be harmful to health, even as the air becomes less humid and less hospitable to mold.
One of the more incorrect statements heard in the mold business: “All the mold is dead.”
Chemicals
Harsh chemicals, when sprayed onto mold, can cause mold to become aggressive — releasing extra spores and toxic compounds into the air.
A typical offender? Bleach, which doesn’t thoroughly kill mold and can even feed it due to its high water content.
Bleach — like other harsh chemicals — will cause mold to release increasingly noxious VOCs and mycotoxins.
Cross-Contamination
Mold spores travel.
Microscopic, they cling to fabrics, float in the air, and even have sticky exteriors.
Spores from a contaminated area can move to a clean environment — often from humans in moldy buildings. The longer time spent in a moldy space, the more spores collect on belongings and people.
“Most people think you have to have a water intrusion or pipe burst in order to grow mold,” Barnes said. “If you have relative humidity above 60 percent and you have organic debris, which we all have, which is dust, you can grow mold.”
Washington Post
HVAC systems inevitably become mold nurseries and spore-delivery systems over time — unless meticulously upgraded and maintained.
It only takes a couple years of neglect for these systems to become breeding grounds of microbial activity.
Without specific upgrades and annual cleaning, the evaporator coils, drain pan, and ductwork will almost certainly harbor mold.
HVAC Design Encourages Microbial Growth
Let’s shine a flashlight directly on HVAC systems. Why are they so problematic?
Two main reasons — ductwork and evaporator coils — and how they interact with dirt and moisture.
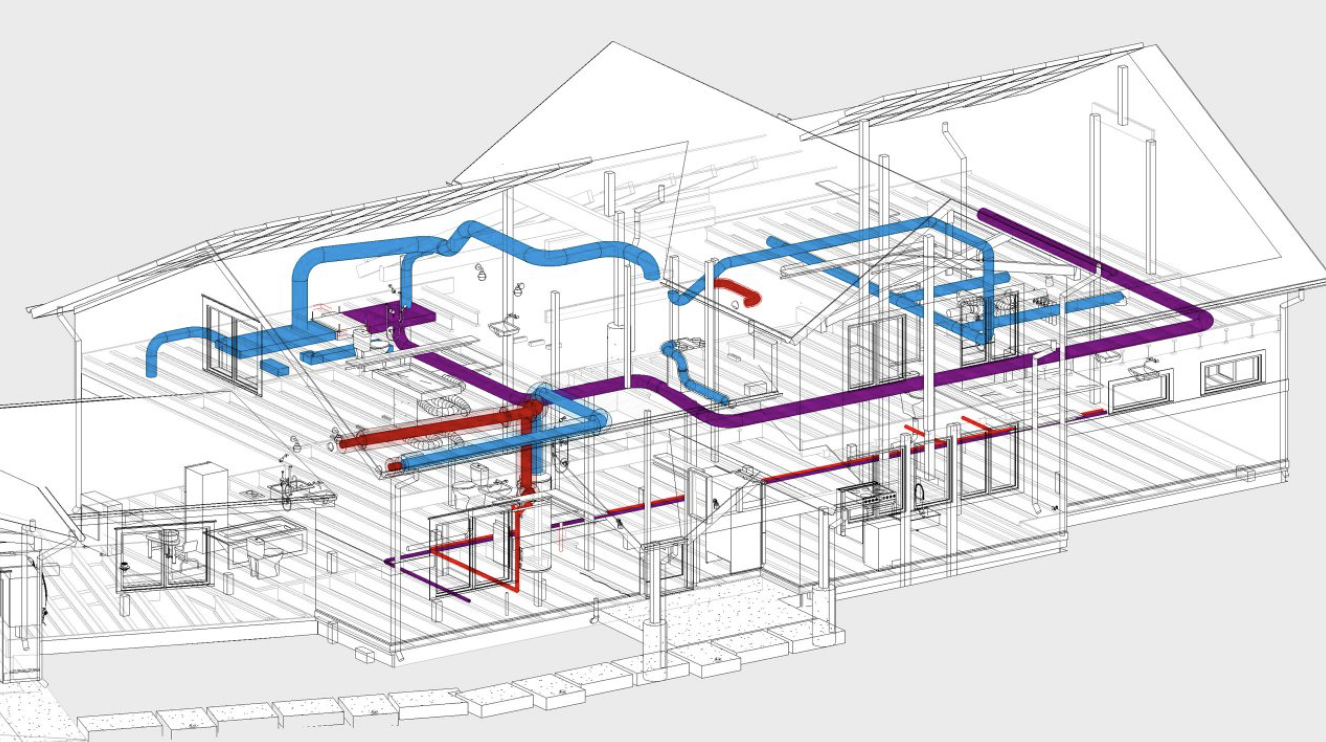
Ductwork
Endless Ducts
There are hundreds of feet of ductwork in a typical home — and thousands in larger homes or buildings.
The air in a building recirculates endlessly, meaning it passes through the ducts over and over and over.

Dust in The Ducts
Dust is kept out of the system via in intake filter (the one you change every 3 months).
Unfortunately, most HVAC professionals recommend a very weak intake filter on a residential system — so as to avoid overburdening the HVAC system. The result — while good for the machinery — is a very, very dusty system over time.
Dusty ducts are not benign! Not only do we breathe the air in the ducts, as condensation develops in the ducts, mold can grow right in the ductwork. Dust and water are perfect mold food.
Moldy ducts mean that constantly recirculated air will contain mold VOCs and spores.
Keeping dust and particulate matter out of an HVAC system is one of the most important steps to prevent future problems.
Moisture in the ducts
Moisture can also be present in ductwork, especially when they are located in attic spaces.
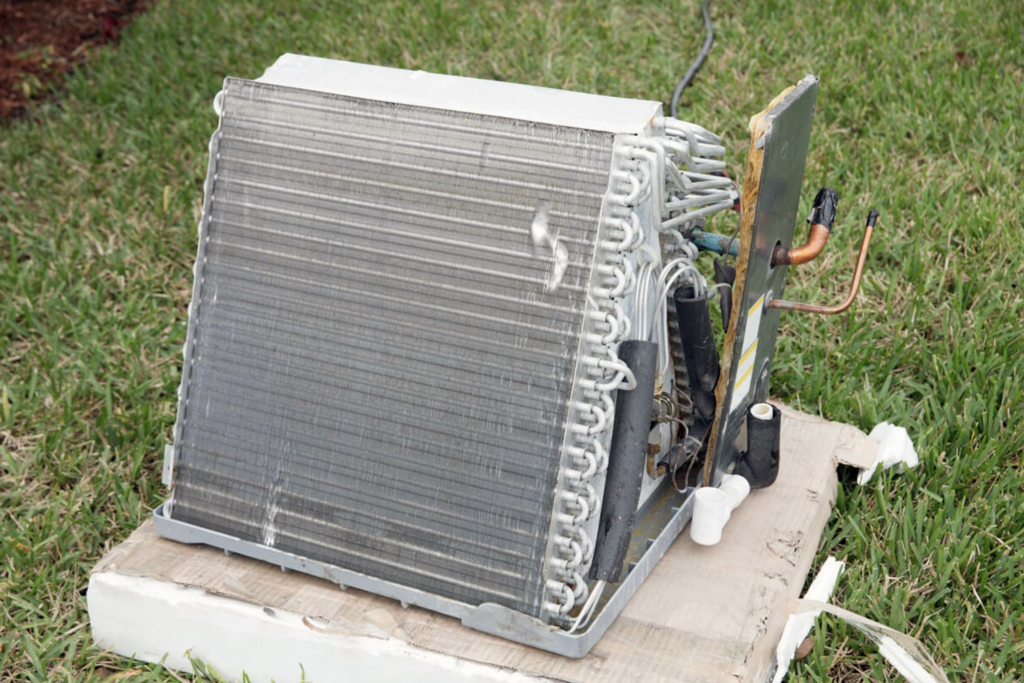
Evaporator Coils in the Handler
Believe it or not, evaporator coils are an even bigger problem than ductwork — and there’s a very good reason for this.
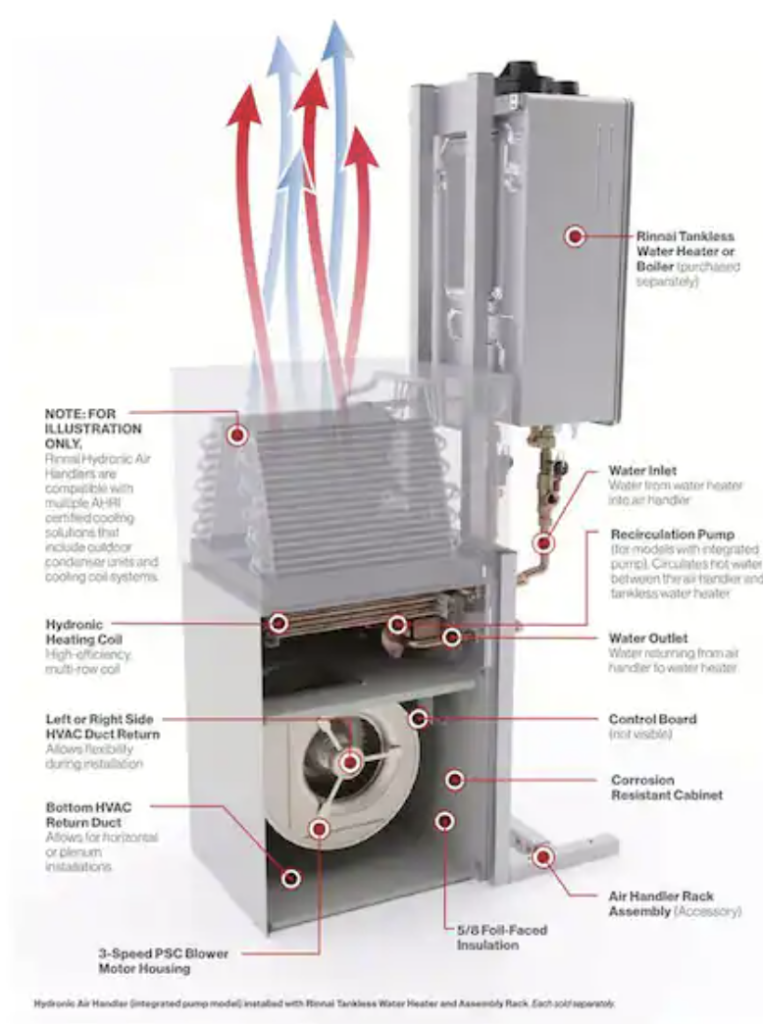
Located in the air handler (in a closet, attic, or crawl space) — the coils rapidly cool the air that passes through the system.
With this rapid cooling, moisture falls out of the air — it condensates — on the coils.

As the system continuously cools, most and more water is pulled out of the indoor air — and deposited onto the evaporator coils.
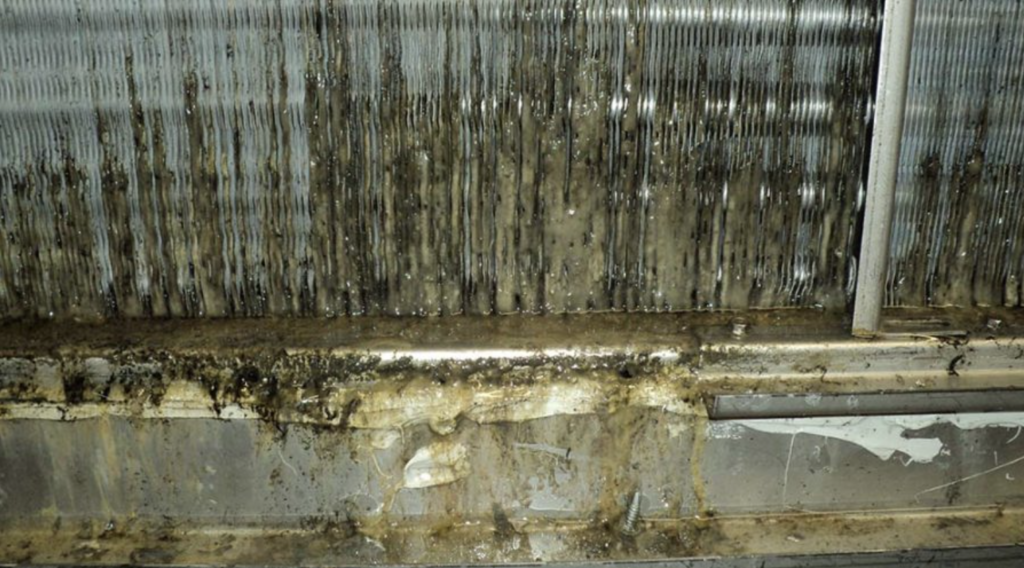
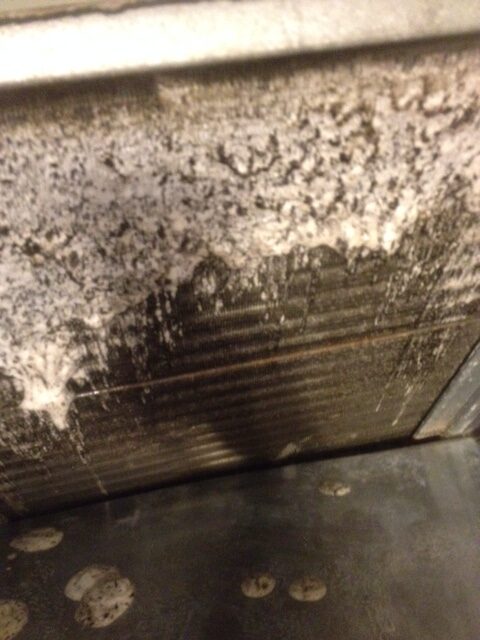
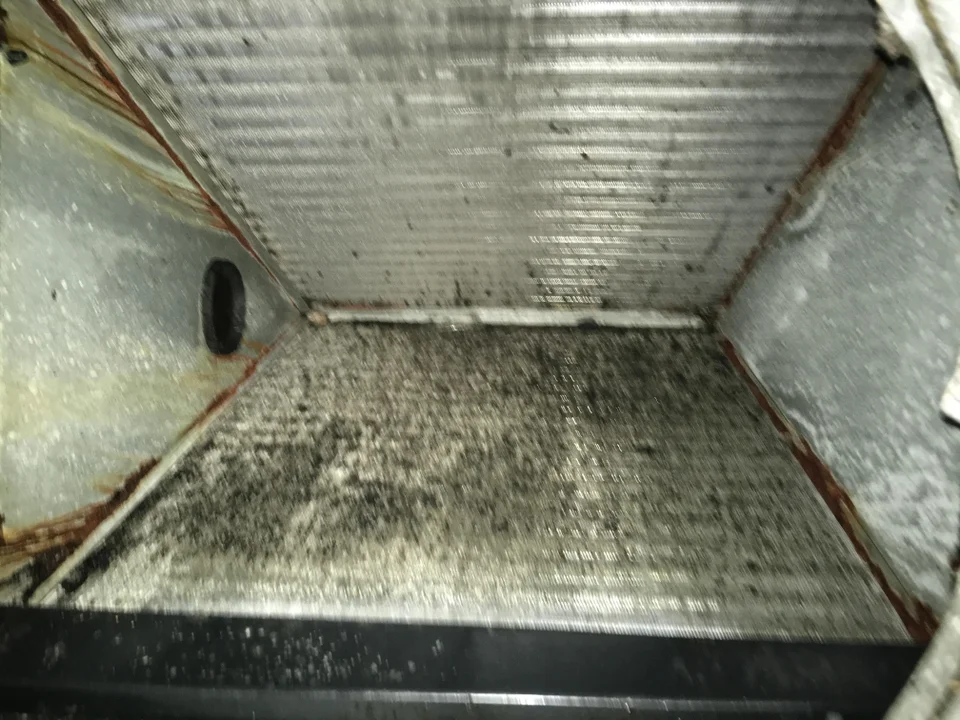




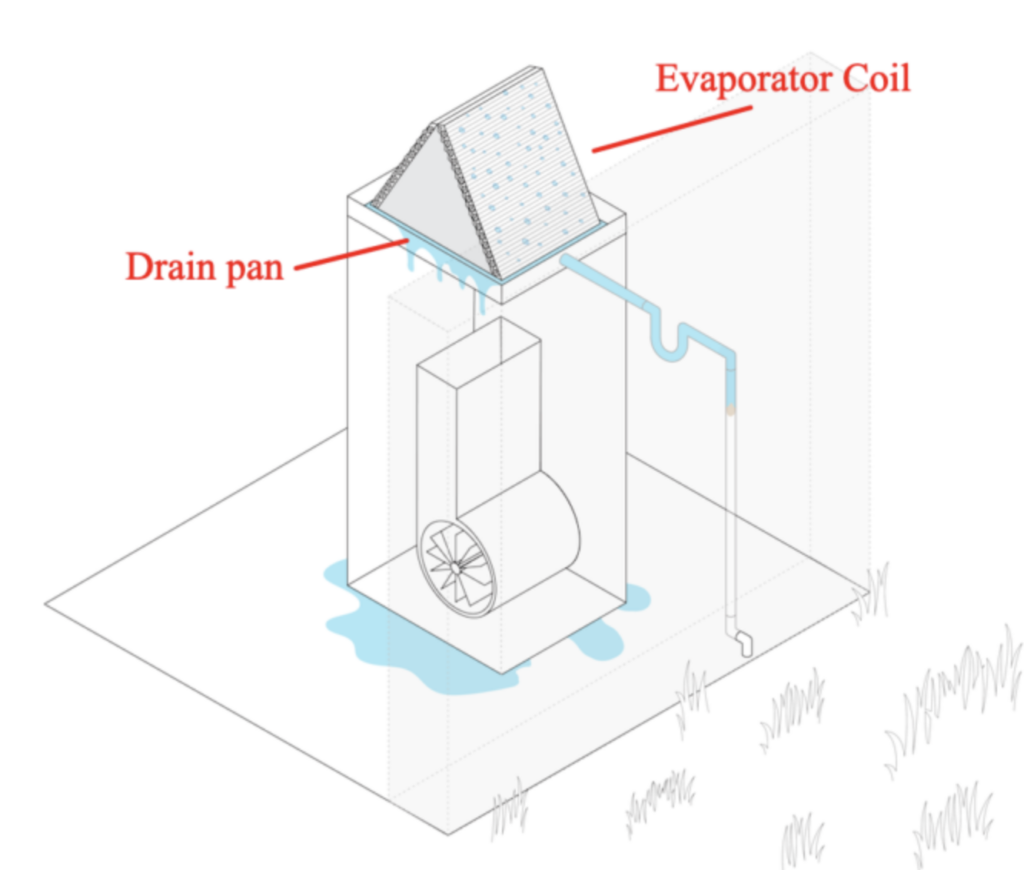
As a result, evaporator coils are virtually always wet during the warm months. Using the system less doesn’t help much — even getting wet just once per day will feed microbial growth.
This moisture (“condensate”) drips down from the coils and onto the drain pan, and runs out the condensate drain (to be discarded outside on the ground).
Therefore, evaporator coils — wet and dusty — are extremely prone to microbial growth.



The single best preventative step to combat moldy coils is a UVC light inside the air handler, shining on the coils, disinfecting the surfaces inside.
Annual cleaning (by an HVAC professional) is also a necessary step to maintain and protect evaporator coils.
How to Find a (House With A) Clean HVAC System

Your best bet for finding a clean HVAC system? A new house.
Upon purchasing, immediately have a UVC light installed, as well as an in-line MERV 13 (or higher) filter installed on the main return trunk (before the air handler).
Prevention is the only tried and true path: Keeping 1) the air handler sterile (UVC light) and 2) dust out of your system (in-line high-MERV filter) is the difference between an HVAC system that ages terribly, and one that stays much healthier for years to come.
It’s also critical to have your condensate drain (and drain pan) cleaned annually, too.
HVAC Systems Age Terribly
If we don’t take steps to protect the system, it only takes months or a couple years for an HVAC system to become compromised — to collect dust, grow microbial life, and then transport VOC and spores all around a building.
Why doesn’t it take very long?
The main reason HVAC systems age poorly — and quickly — is the sheer amount of dust, dirt, & spores in the air, combined with the incredible amount of moisture that is pulled out of air (when cooling).



An HVAC system — especially the evaporator coils — are constantly exposed to dirt and water, the two ingredients required for mold growth.
Also, beware of over-powered units. Too much power means humidity won’t be pulled out of the air before the unit shuts off its cooling cycle. This can cause condensation around the house and inside the ductwork, too. HVAC units must be sized properly for the space they are in, especially not too large.
“…while mold in a house is often found on walls, floors, ceilings, carpets and fabrics exposed to moisture, one particularly troublesome hiding place is inside the ductwork and associated components of central forced-air heating and air-conditioning systems.”
Jeffrey May,
(My House Is Killing Me: The Home Guide For Families with Allergies and Asthma”)
New York Times, 2001, Jay Romano

HVAC Systems are dark, hidden, dust-collecting chambers. They are extremely difficult — if not impossible — to adequately clean. They create constant condensation (on evaporator coils, drain pan, and sometimes, in ducts). All of these factors feed microbes — particularly mold.
HVAC at Local Nashville Locations
When mold growth happens inside the HVAC system, it won’t remain there indefinitely. Mold is highly adept at spreading to new places — via spores.



All HVAC Systems Must Be Maintained
When HVAC systems are fully serviced every 6 months, this should include a full cleaning of the evaporator coils, drain pan, and drain line.
Cleaning Evaporator Coils
HVAC technicians often loathe to clean coils, and it’s understandable: It’s a messy job.
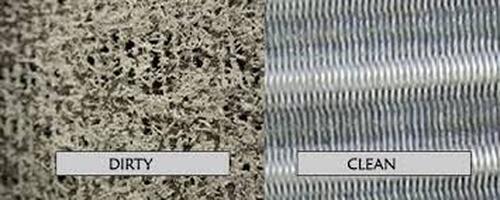
Unwilling HVAC Technicians
Don’t be surprised if a technician attempts to talk you out of coil cleaning.
They may invent reasons you don’t need it (it will harm the coils, your coils look great, etc). Either insist you want the service, or find another company who is willing to do it.
You might request before and after photos to ensure the job was done well (it might be tempting for a tech to skip the treatment, but inform you it was done). While I don’t recommend lying, I also don’t recommend insulting tradepeople. Therefore, if you need to, you might invent a reason for the photo request, such as insurance, documentation if you sell the house, etc. (All of those reasons are valid).
Cleaning Ductwork?
Some people say ductwork should be cleaned regularly — but that may not be wise advice.
While ducts are long, narrow, inaccessible chambers and virtually impossible to truly clean after they have been contaminated by mold, if your system is protected from dust, and has a UV light installed, you very likely will not get mold growing in the system.
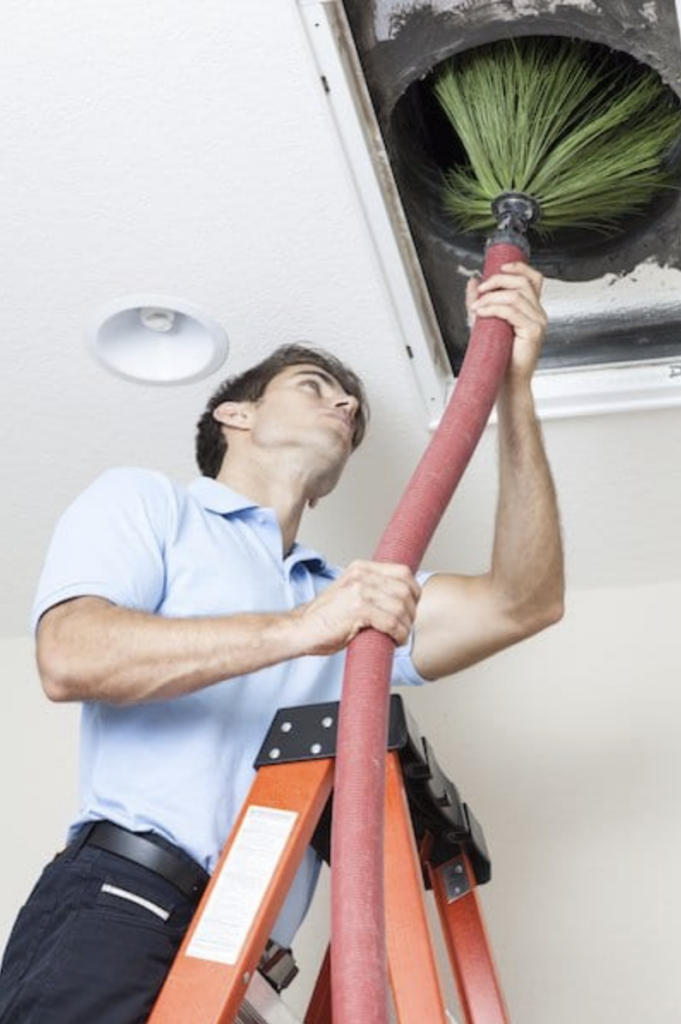

If you have very clean ducts, I see no reason to introduce cleaning brushes — which have likely been in hundreds of other, probably filthy, house’s ductwork — into yours. If anything, cleaning ductwork that doesn’t need it could introduce mold spores into your system.
If your ductwork is already compromised, a cleaning might help some. However, anecdotal reports (and sound logic) both suggest duct cleaning is not a complete solution to problematic ducts. The only total solution is to replace ductwork — a very, very expensive job. Yet, if mold growth is occurring elsewhere in the home, a new HVAC system can become re-seeded with mold spores rather quickly.
Change Filters
Be sure to change your default return filter(s) on time (3 months or so, depending on build-up), and if you install an in-line filter (on the main return trunk), change its filters as well.
What filter rating should you use? If you don’t have an in-line filter installed (in the system), and only have the default return filter, use a MERV 7-10. Higher will put strain on the system, lower will allow in excessive dust. There’s a tradeoff: Keeping the system more clean -VS- reducing strain on the system. Because of health reasons, I lean toward keeping the system more clean.
HVAC UVC Lights
UVC lights are essential to discouraging mold growth on the evaporator coils — and their installation is quickly becoming an industry-standard practice.
The bulbs can be installed inside the handler so that the coils are constantly exposed to UVC light, making mold much less likely to grow.
Unfortunately, UVC lights are best for prevention and will not totally solve a problem that’s already occurring (although they will certainly help, especially in conjunction with professional cleaning of the coils).
Are Ductless Mini-Splits a Good Option?
Ductless mini-splits are growing in popularity. At first glance, they might be a better option than HVAC systems. Why? Because they don’t have all that problematic ductwork!
Instead of one large air handler that cools the air for an entire floor, ductless mini-splits place a small air handler in every room.
The evaporator coils also create condensation when air is chilled, and dust can still enter the unit — so they must be fully cleaned every 6 months. Each unit has a filter which must be replaced every 3 months.
So, while ductless mini-splits avoid the pitfalls of ductwork, they also decentralize potential problems instead of quickly spreading one problem to an entire building.
But ductless mini-splits are not easy to clean. They must be completely taken apart, and it’s not easy — even for professionals — to totally clean all the intricate surfaces inside.
What’s more, most mini-splits do not have the capability to install a UVC light inside. This is a real issue.
I personally would rather have a new HVAC system with a UVC light, than a new mini-split without one. With an extra in-line filter, I can keep ducts clean — and a UVC light will always better keep a clean system clean. It’s just too risky to have evaporator coils without a UVC light to protect them.
Mold is only a problem in older, poorly-maintained homes… Right?
After all, with newer homes there has been:
Unfortunately, there’s more to the story: Modern construction practices, consistency of proper installation, and materials are different from the past… for better and worse.
In fact, in building biology circles, modern homes are often referred to as “mold candy” for the following reasons.
Mold Sprouts on Materials Before Install
Many building materials have already developed mold before even arriving at the construction site.
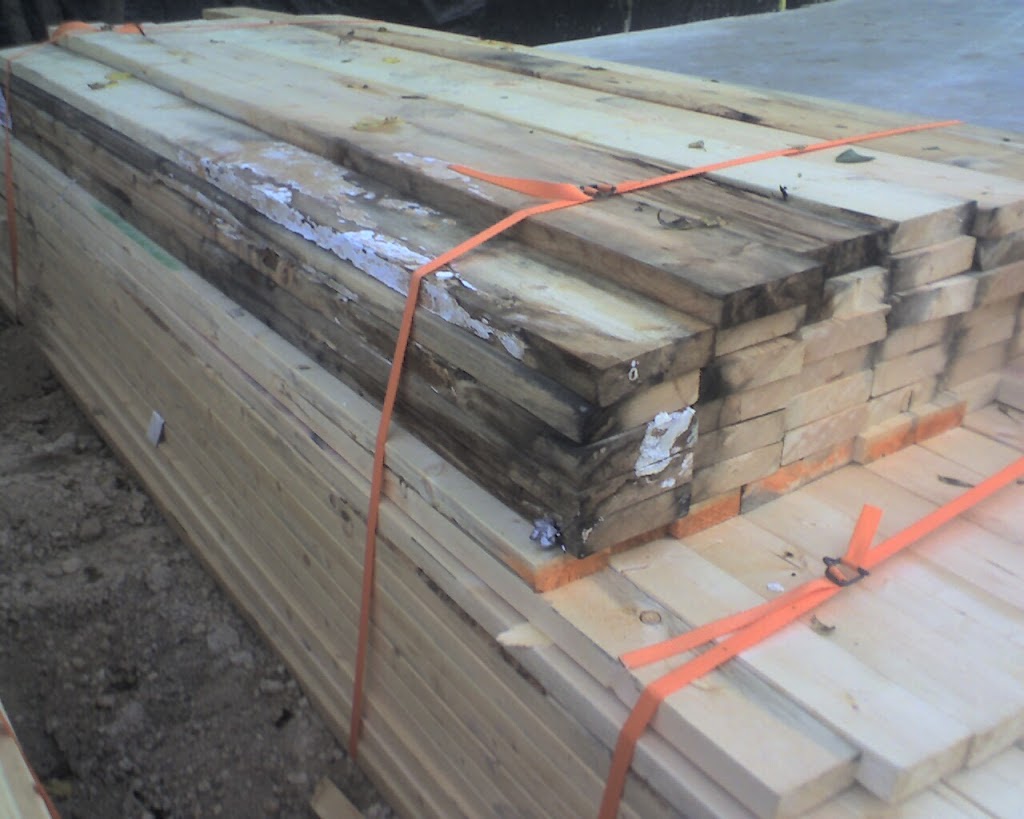
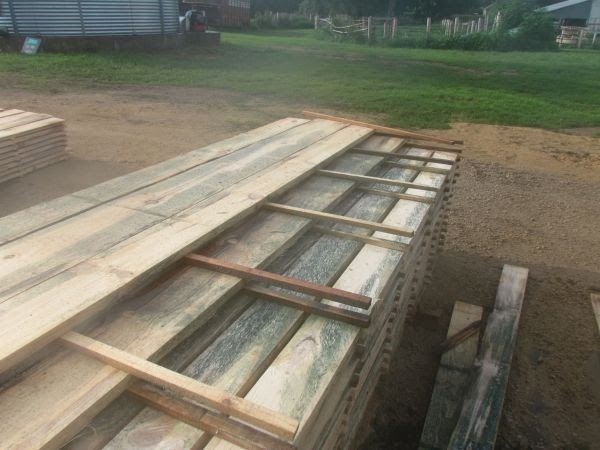


Here’s a worst case scenario: Materials are sometimes left uncovered for a few rainy weeks at a supply house yard. They’re then left exposed at the building site during more rain. Bad weather — or poor planning by the GC — can leave a house exposed to the elements before the house is “dried in.”
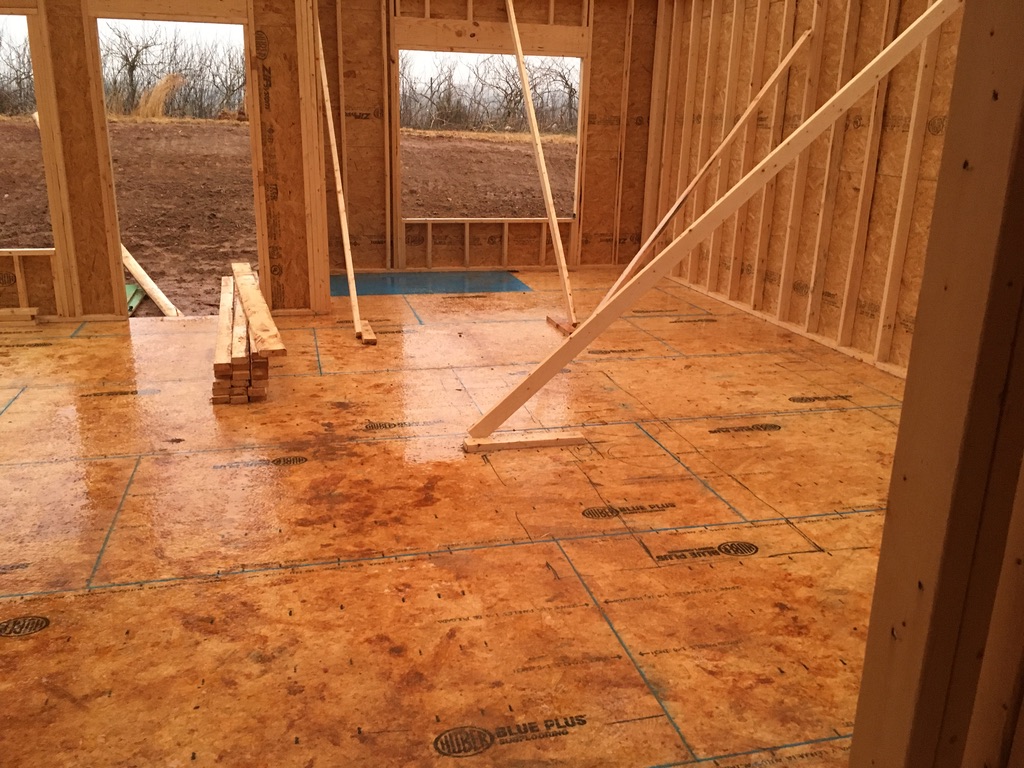
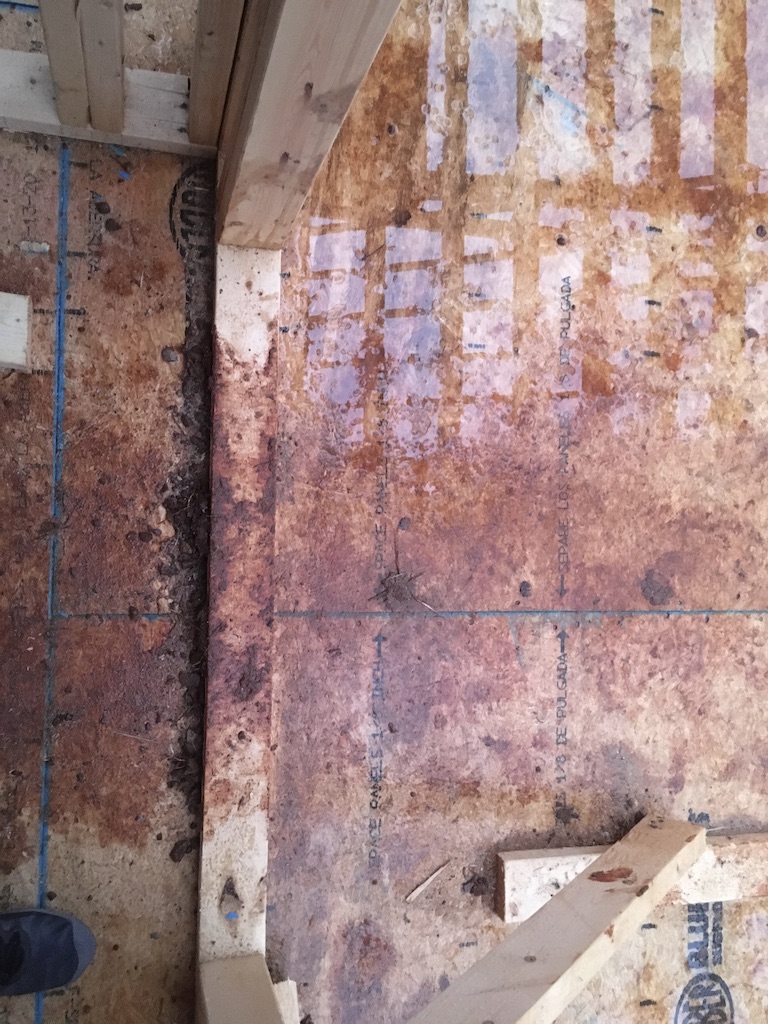


Once mold begins on a building material, it will never go away, it won’t die (and even if it did, it releases millions of spores all over the area.
OSB & “Pre-Digested” Wood Products
OSB (oriented strand board) is then used throughout the house, and drywall is installed.
OSB and drywall are prime examples of “mold candy” due to heavy processing of the materials.
Both OSB and the paper that lines drywall have very little tolerance to moisture, and quickly feed mold if they ever get even the slightest bit wet.
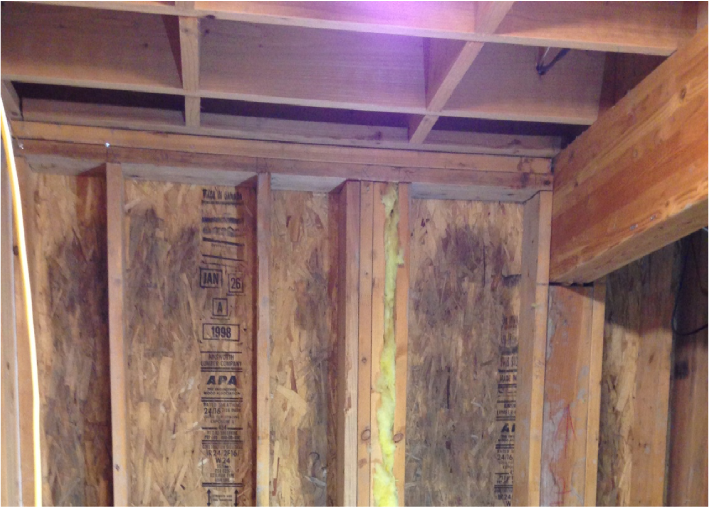

Construction materials are repeatedly processed to break down the wood’s fibers. This creates a highly digestible food source for mold.
In many climates, all unconditioned spaces (attic, crawl spaces, garage) are subject to high humidity at various points in the year — even with proper ventilation.

New Homes Are Built “Tight”

Modern homes trap air, which accumulates chemicals, toxins, dust mite excrement, and VOC’s — while oxygen levels fall.
This air-tightness also can trap humidity inside the building’s envelope, preventing it from drying out.
New energy-efficient homes tend to be conducive to mold growth because of their tightness, which restricts air movement.” They’re too green,” said Nelson Barnes, Jr., a mold remediation expert in the. Washington area. “Houses need to breathe.”
Washington Post, October 25, 2013
Extreme temperatures can cause mold as well:
Homes on Concrete Slabs
Concrete slabs have a huge advantage — no crawl space for foul air to collect as a result of mold growth.
However, homes on concrete slabs can experience high humidity in the first year — as the slab releases its moisture over the first 12 months after pouring.
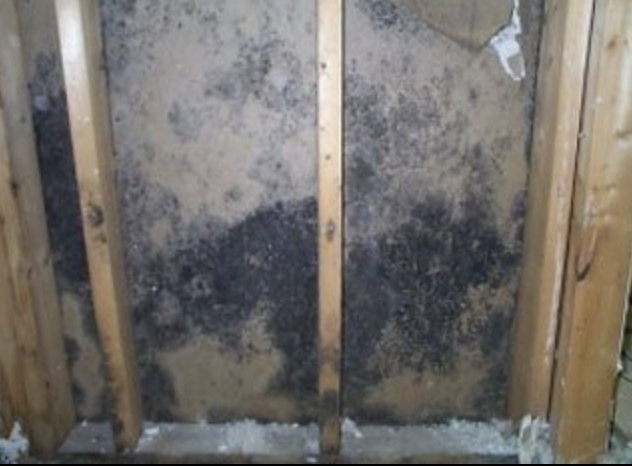




“Contractors may begin to notice mold growth on the 2×6 walls and sheeting/siding if they take the time to notice. Unfortunately, most of them will not take the time to do so.”
NEW CONSTRUCTION MOLD: A RISK TO NEW HOMES

Should You Avoid New Homes?
No — new homes are often the safest bet when purchasing a new home.
That said, it takes a keen eye to spot problems — and many are only visible during construction, before the walls are closed up with drywall.
If you can’t inspect during construction, you’re always taking a risk when buying a finished home (new or old).
A new house with a few problems during construction likely won’t have a mold problem at the time of completion. But, those few problems could lead to issues down the road.
I would still, at the end of the day, when it comes to building health — in America, where lumber is the primary building material — choose most new homes over most old ones.
Was Older Construction That Much Better?
Actually no.
OSB has been used for decades. Shower wall waterproofing was non-existent as late as the 90s and 2000s. Window flashing has only recently become a focus (though most builders still aren’t executing this well).
A few advantages with older homes? Homes weren’t built quite as tight, which prevented humidity from being trapped. Lumber quality was better, and resisted mold a bit more. Crews weren’t pressured to work quite as fast as they now. Tradespeople sometimes had a bit more skill, as they were installing more rudimentary products that required more focus.
Generally speaking, though — and it took me a long time to come to this opinion: Despite the disadvantages, modern construction typically produces a better product than older methods.
How well building products are installed is by far the most important variable during construction.
Modern homes work hard to keep water out — via roofs, weather barriers, flashing of penetrations, and the dehumidification effects of HVAC.
And yet, water is piped right into the house — via plumbing.
Modern plumbing is usually a plastic material called ‘PEX’, a type of plastic.
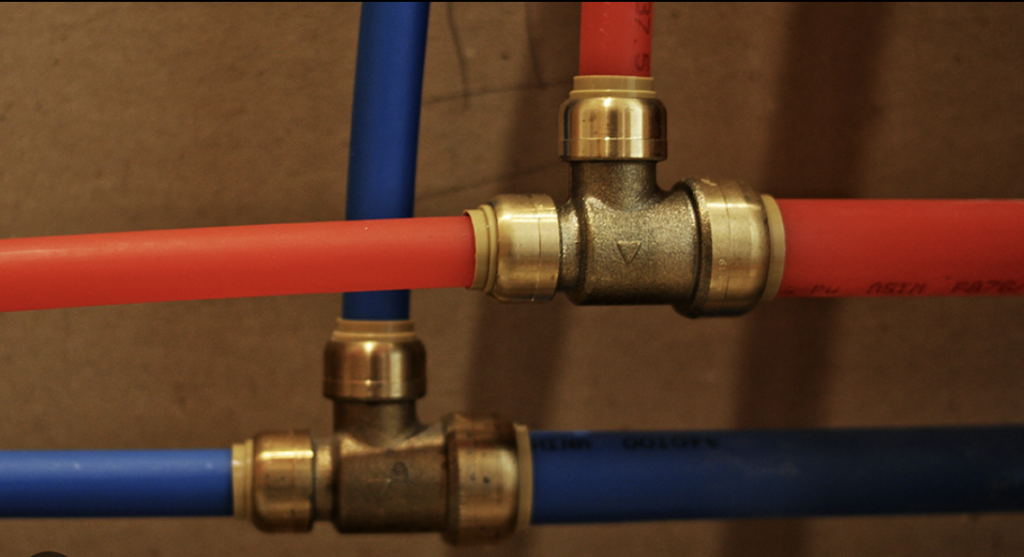

PEX replaced copper pipes, and before that lead pipes.
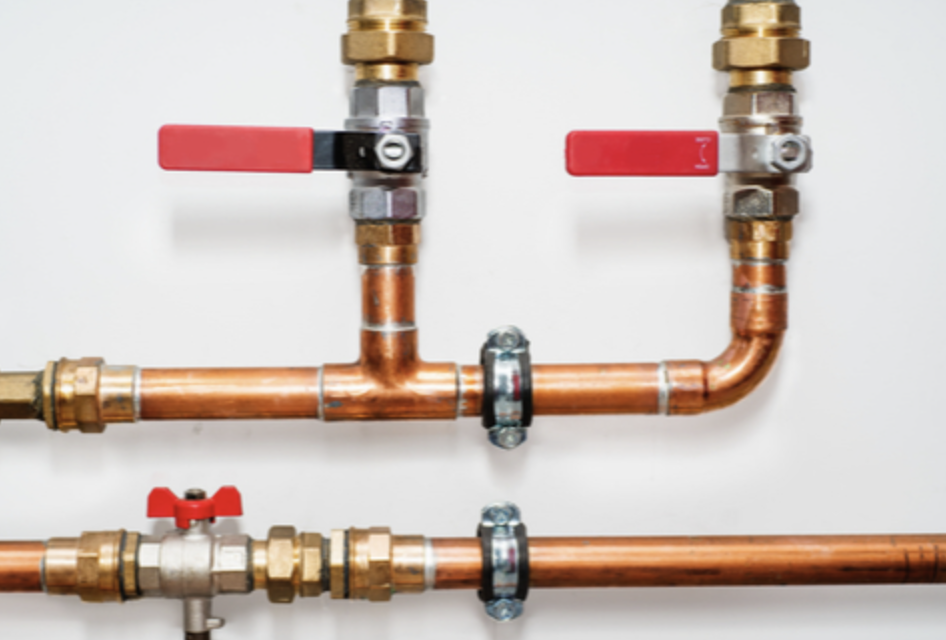

PEX is less likely to leak than previous technologies, but still leaks over time. Installer error with any pipe can lead to tremendous leaks.
Leaks almost always happen where there is a fitting. A fitting is any type of component that connects one pipe to another pipe. Here are examples of fittings:
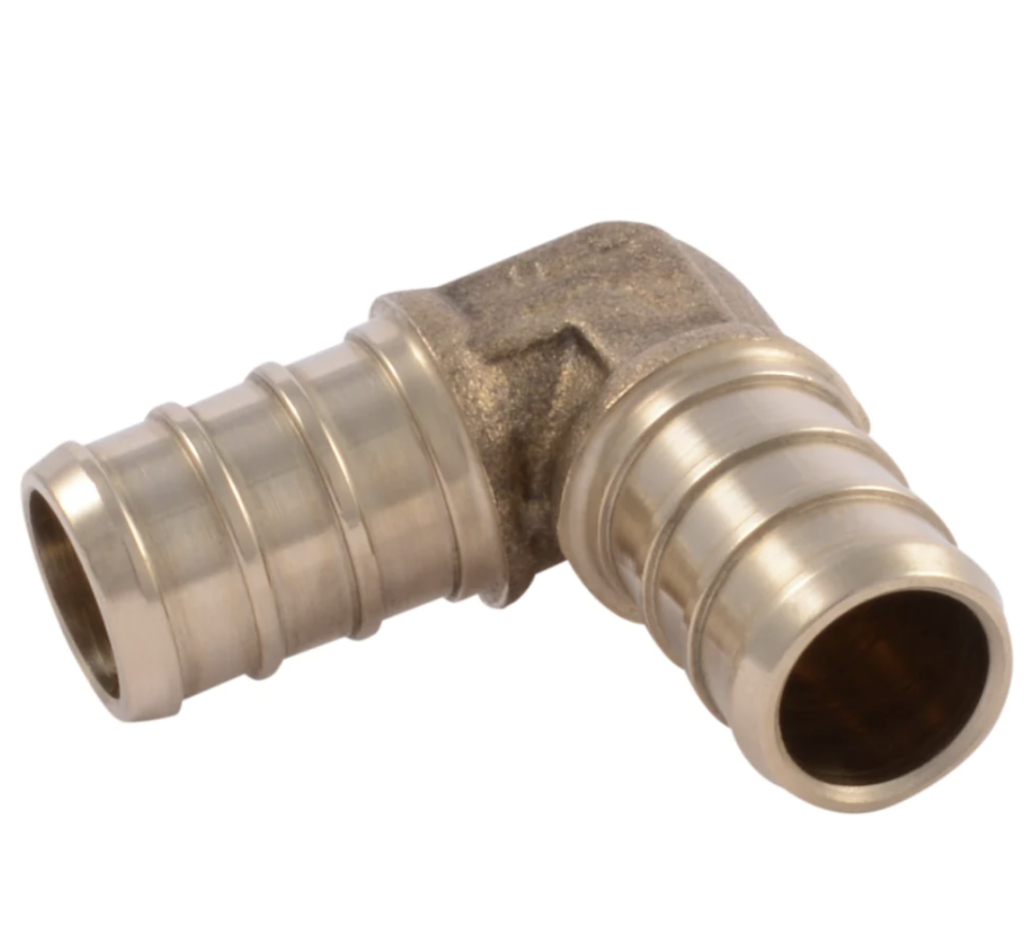
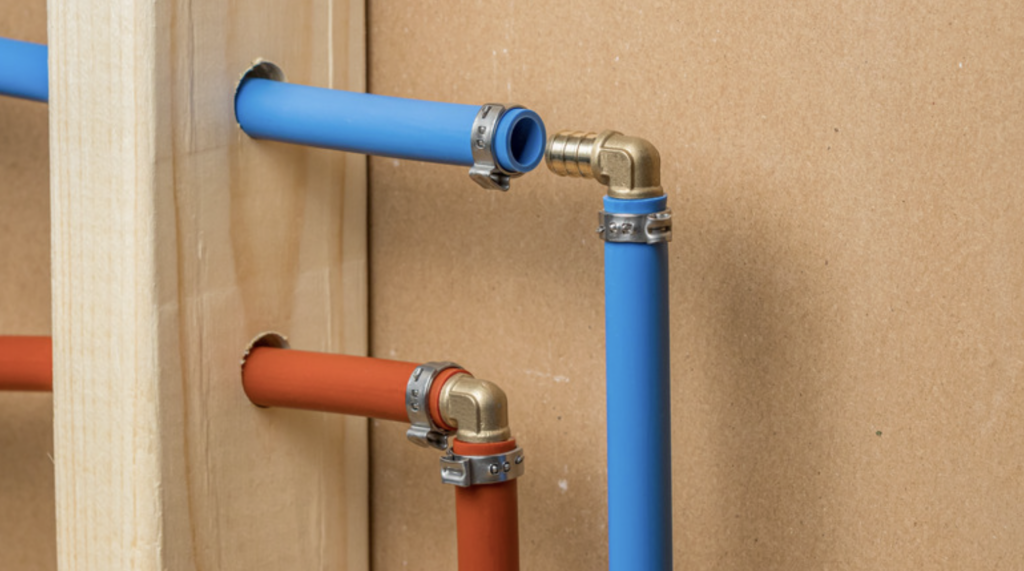
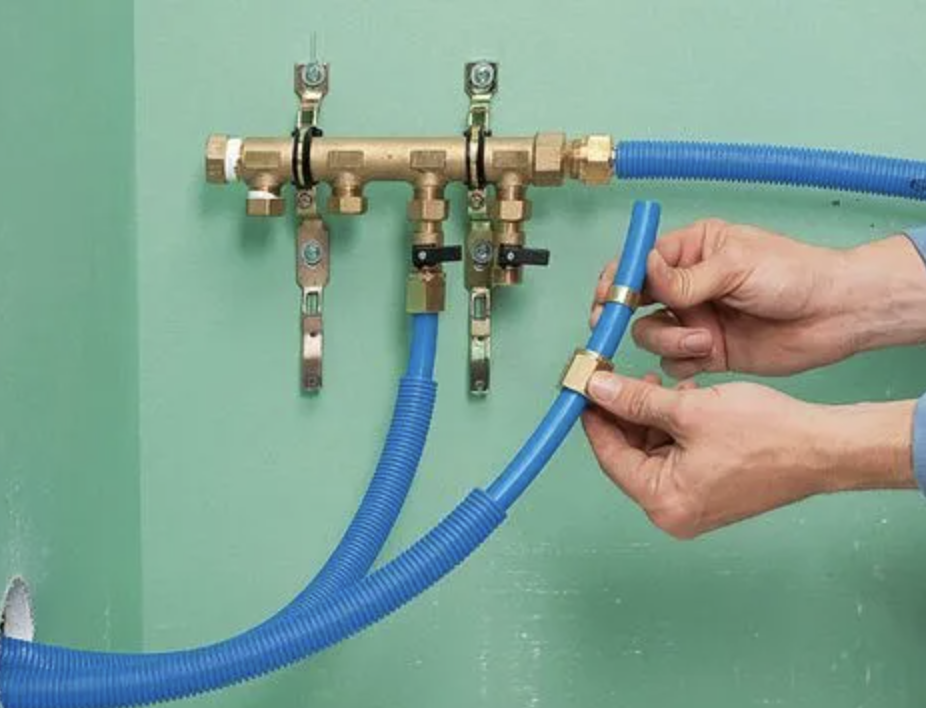
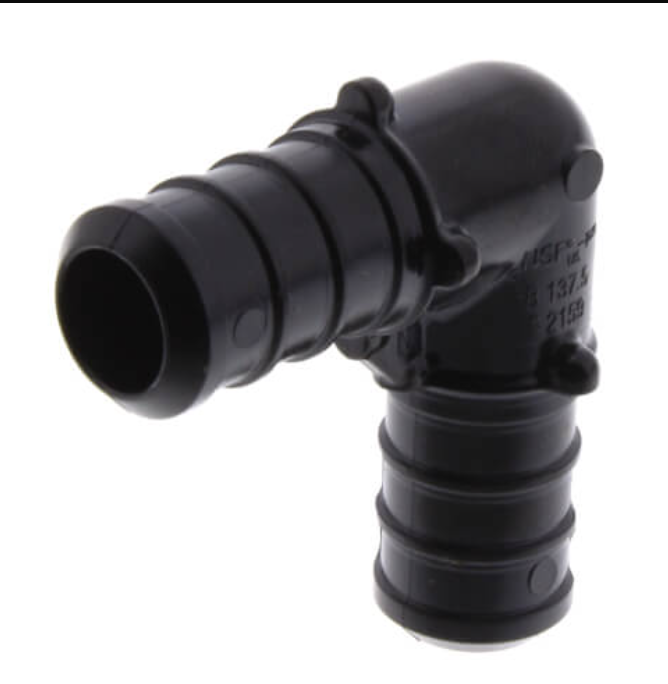





Fittings can be metal or plastic. Some require “crimping” (squeezing with a tool) to latch, others simply push-to-connect.
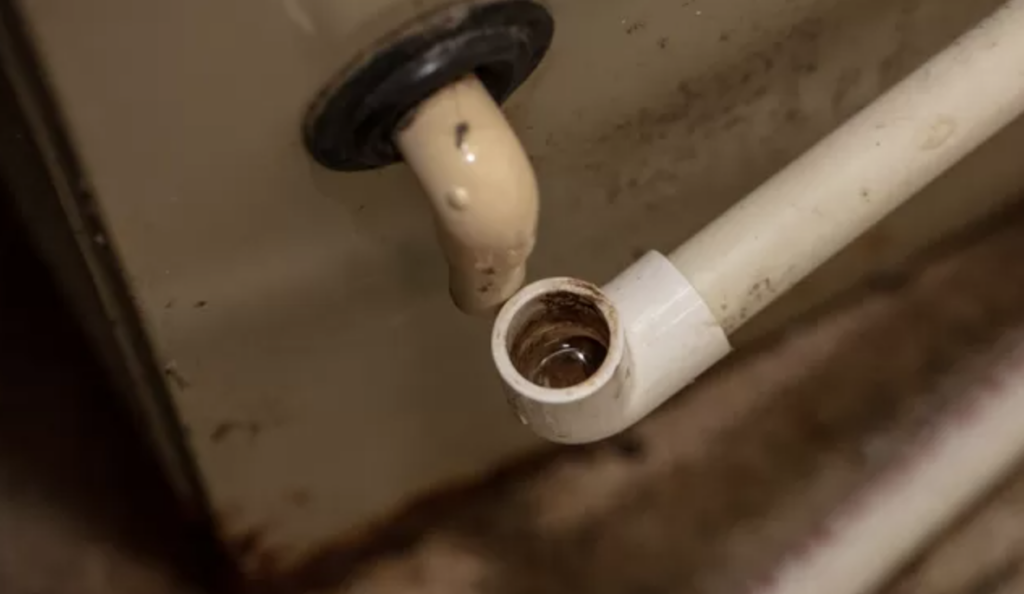
Fittings can leak — they are the most common places for leaks to occur. Fittings can be found inside walls (not viewable), and inside cabinets (viewable).
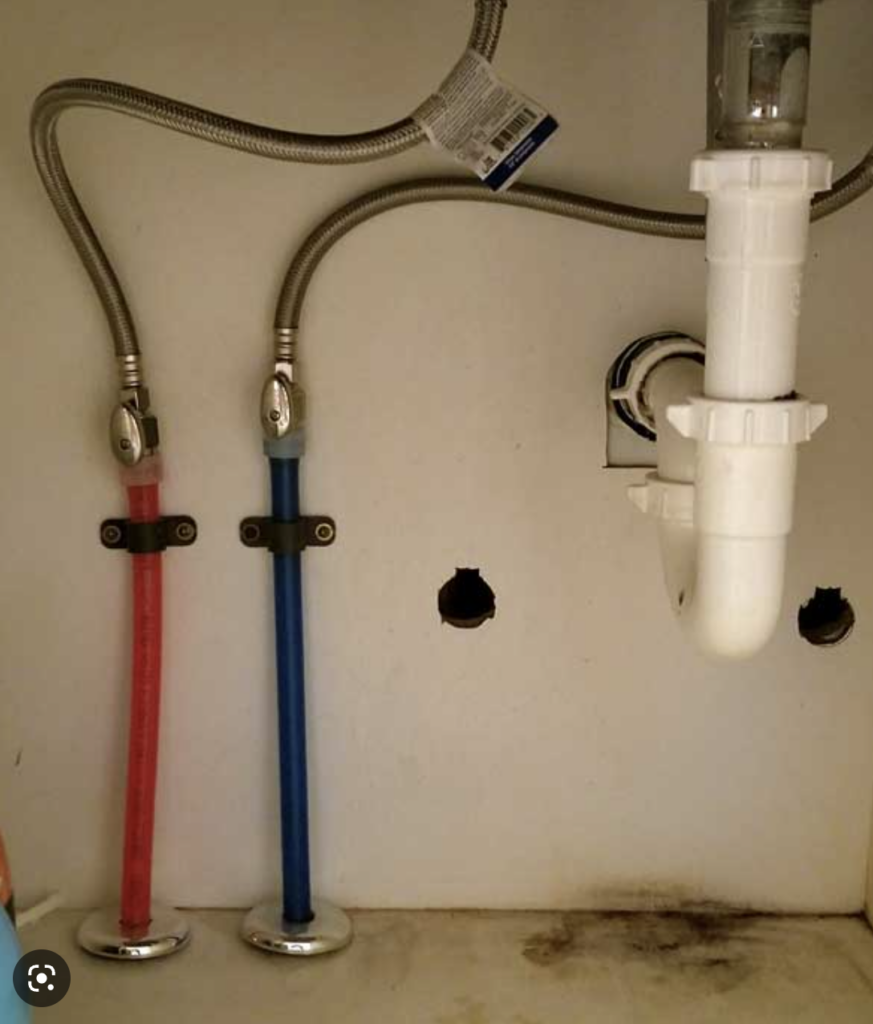

Above, PEX pipes (red for hot | blue for cold) bring water into a vanity. Fittings connect the PEX pipes to the gray connector hoses.
If you look to the bottom right, there are signs of mold growth from a recent leak. Cabinets with sinks are a major problem zone for leaks — and mold growth.
All Plumbing Fixtures Are Potential Leaks
A “plumbing fixture” is any machinery that is connected to the plumbing system.

This includes all faucets, drains, washing machines (laundry & dishes), showers, baths, toilets, hose faucets. Air conditioning units qualify because they have drain lines, although they aren’t connected to the main plumbing system. Anywhere there are plumbing lines, there is water — and the chance for leaks.
Plumbing in a New vs Old House
All plumbing is prone to leaking. So why does it matter if I have an old house or a new one?
Several reasons!
Older homes might have copper pipes, which are more prone to leak than newer PEX.
Older homes also have had more time to be exposed to leaks. And if those leaks weren’t handled well — or immediately — old mold problems can be hiding literally anywhere in the house.
New houses aren’t exempt from leaks. I once saw a house have 9 leaks in the first year after it was built. This was an anomale, though; work performed by a very bad plumbing contractor, who later fired the lead plumber who did the work.
What’s more common is that most houses with have a leak, of some sort, within the first 3-5 years. But that’s also true for old houses. Leaks happen, regardless of the age of a house.
6
Problem Zones
Where Should You Look For Mold?
Anywhere moisture or elevated humidity (above 55-60%) can be found.
Older Homes
Even if an older home was built better, time is not on its side.
More time for mistakes & accidents where water damage can occur. Even worse: if water intruded and the owner did not address the problem rapidly or appropriately.
Newer Homes
New construction is often rushed, and mistakes can be made. Inspection during the build is the only to know whether it was built right.
Carefully look for plumbing leaks after moving in.
Make sure the grade around the house falls away from the structure.
Inspect the attic for clues to the quality of the build — is the wood clean? Does the framing look sloppy? Do you see moisture intrusion?
Garages
Garages trap air, humidity can rise.
Moisture can be introduced any time the door is open, or by wet cars. Garages are rarely kept clean. Dirty items get stored here.
Unless sealed off, air from attached garages will always find its way inside a home — bringing down the home’s air quality.
Basements
Basements face a lot of pressure from moisture — from both ground water below and rainfall above. As a result, they are almost always leaking water inside. Basements can be very risky for building health.
Crawl Spaces
Crawl spaces can trap humidity and foster mold, even when properly ventilated. Crawl spaces MUST be encapsulated to reduce humidity.
Grade must slope away from the house. Water cannot be allowed to stand around the building’s foundation.
Attics, Sheds, Storage Units, and Boiler Rooms
These areas facilitate trapped, humid air.
Bathroom exhaust fans should NOT send humid air to the attic.
Preventing mold in these danger zones requires active awareness and ongoing maintenance.
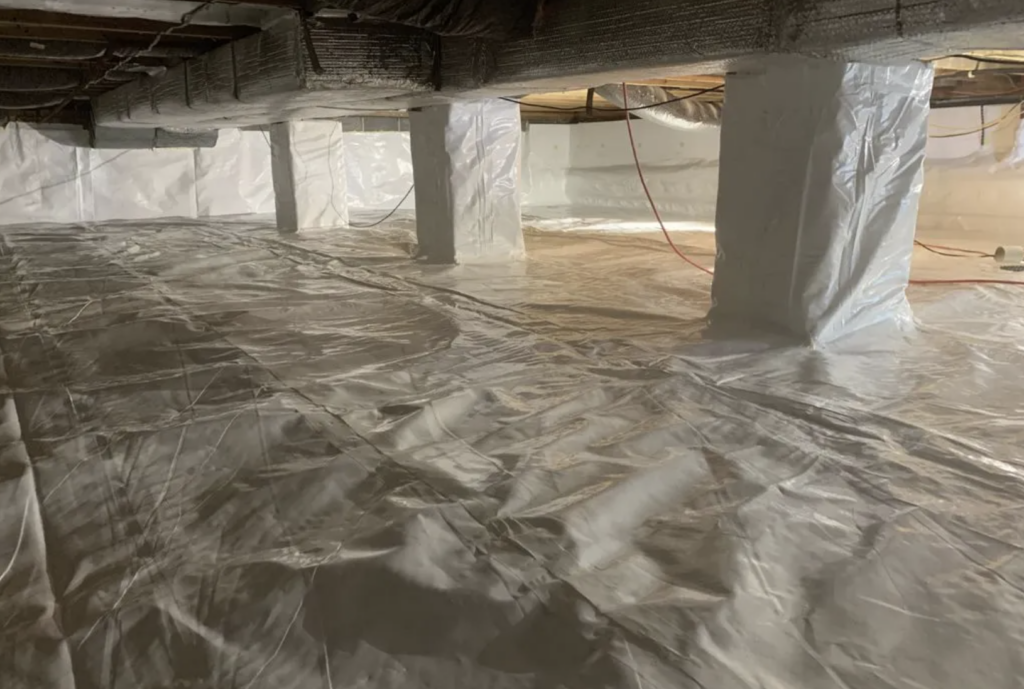

Don’t Let “Difficult to Access” Mean Difficult To Monitor
Modern comfort and convenience have encouraged an “out-of-sight, out-of-mind” mindset that, despite its societal prevalence, is remarkably unwise.
Get to know your house and other buildings — and check on them frequently. Stay on top of all building maintenance; We don’t have the option not to!
Almost every type of symptoms seems to be associated with mold illness — perhaps for a reason.
Mold seems to affect two very important bodily systems: the gut microbiome, and inflammation.
When the body is inflammed chronically — as can happen with ongoing mold exposure — all of its vital systems are affected negatively:
One’s health status when first exposed to mold — along with the severity of the exposure — influences how well, or how poorly, someone responds to mold exposure.
Other factors, like emotional trauma and genetics can further determine one’s resilience (or lack thereof) to mold exposure.
Inflammation
In many people, mold exposure appears to cause inflammation to rise high and remain high chronically.
Chronic inflammation affects nearly every bodily function: hormones are severely disrupted, nutrients aren’t absorbed, mental clarity can be lost, sleep is broken, and blood sugar can be dysregulated.
For every essential bodily function, chronic inflammation gets in the way — and this is one way one simple thing — mold toxicity — can affect your entire life.
Gut Health
Mold — with its spores and mycotoxins — has the potential to wreak havoc on gut health.
Chronic inflammation is not good for the gut, not at all. Inflammation blunts the gut’s ability to properly absorb nutrients (source).
Even acute inflammation interferes with gut health.

What’s worse, fungal spores can take up residence in a weakened — and therefore (too) hospitable — gut. After all, trillions of microbes per day are swallowed via the mouth.
Now, scientists have found that even in healthy people, many mouth microbes are able to reach the gut and colonize it.
https://microbiomepost.com/many-gut-microbes-could-come-from-the-mouth/
Even without the presence of mycotoxins, impaired gut health leads to overworked detox organs like the liver, kidneys and lymph system because metabolic waste and microbial endotoxins cannot be eliminated properly. Instead of daily excretion, toxins wind up reabsorbed into the bloodstream, to cause more inflammation. This only worsens as gut health declines and fiber — which traps toxins in the gut for excretion — becomes less and less tolerable.
And when mycotoxins and VOCs from mold enter the picture, the liver’s burden on grows.
This can result in worsening food intolerance over time. As gut health declines, eating feels more and more hazardous — and for good reason: In gut dysbiosis, you are poisoning your body and causing serious inflammation every time you eat.
Compare this to a healthy gut: Good flora ferment your food, releasing nutrients — B-vitamins, butyric acid and Vitamin K2, strengthening the body’s metabolic processes.
Probiotics make nutrients more availabe to the body. Pathogens in the gut do the opposite: causing endotoxin & inflammation instead.
Sleep
Mold exposure can destroy sleep.

Chronic inflammation disrupts the conditions required for sleep.
So does nutritional deficiency — from impaired gut function.
General toxicity is often a cause of poor sleep. The mold sufferer often has high glutamate in the body, making it difficult or impossible to relax.
(Do not turn to benzodiazepines for sleep, they are extremely harmful and cause cellular change that can require months to undo).
During sleep, the brain dumps waste and toxins; The sleep-deprived person essentially has a toxic brain. This can make cognition and emotional regulation very difficult.
The end result of poor sleep — on top of low immunity and poor digestion and low energy — is difficulty interacting with others.
Chemical Sensitivity
Mold sufferers often become increasingly sensitive to environmental triggers, such as chemicals, pollution, smells, and VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds).
An over-active inflammation/immune response is to blame. The brain identifies compounds as “dangerous” and reacts strongly against them.
I suspect this is because of the aforementioned failing nutritional absorption, rising bodily and brain toxicity, chronic inflammation, as well as chronically elevated stress hormones (which are needed to provide the body with energy when gut health is compromised and thyroid function is suppressed).
Mast Cell Activation Syndrom (MCAS) and Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (CIRS) are fitting diganoses, here, though they are all linked to the gut microbiome, nutrients, detox, sleep, and more.
Blood Sugar Crashes
Inflammation, toxicity, and nutrient-scarcity lead to blood sugar instability.
Poor sleep makes blood unstable, too.
Unreliable blood sugar is extremely common, and usually isn’t fully healed until gut health, toxicity, nutrient stores & balance (including fat solubles, minerals, and B-vitamins), and sleep improve.
Getting clear from major sick buildings is critical, as well.
Diet plans that avoid carbohydrates are often counterproductive in this state (or, at all), as they do not succeed in “starving” out gut pathogens, yet do create weakened conditions for the whole body through over-reliance on stress metabolism.

Recovering from mold illness is a process that involves getting clear of exposure, and healing the body and mind together.
Read more about recovery:
The Simple Answer
Mold is most dangerous when moisture is chronically present in a house.
When mold is growing, there are four variables that determine how dangerous to your health the exposure will be:
(1)
Intensity of Exposure
The extent of the growth, your proximity, and indoor air flow all contribute to the severity of the problem.
Extensive Mold Growth
Mold growth becomes extensive under the following conditions:
- Heavy moisture intrusion
- Long-term moisture intrusion
- Low-quality building materials
- Low-quality building design
- Poor maintenance
Proximity
How close we are to mold growth in a building can affect our exposure level.
- Mold near the bedroom is certainly a more direct threat than out in the garage (although once in the garage, it will spread).
Cumulative Effect Of Multiple Species
- Less-toxic molds might still be harmful if growth is heavy
- Less-toxic molds might still be harmful if many species are present
- Even bacteria (not mold) can grow in wet areas, releasing noxious gases
Trapped Air
- Poor air-exchange and trapped-air spaces can accumulate toxins rapidly
- Modern houses are very tightly sealed, with poor air-exchange
(2)
Duration of Exposure
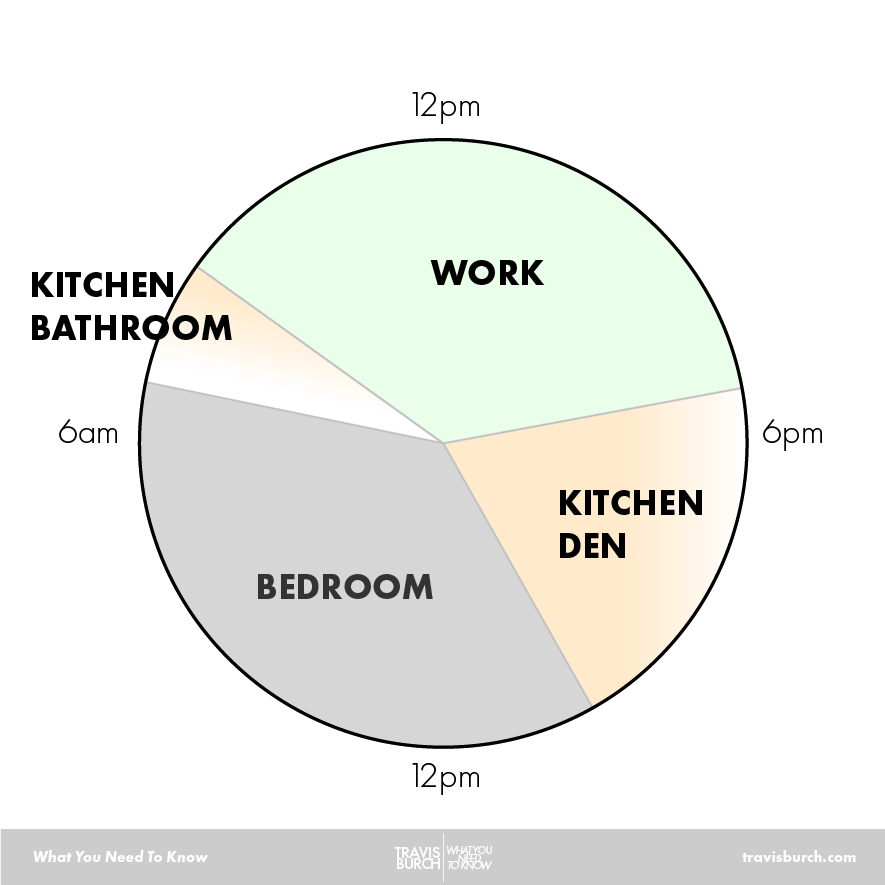
The more time you spend in a sick space, the more time it has to affect your system.
Were you exposed for mere days? Months? Years?
Even the room you were/are in can affect how much time you spent exposed:
- Bedroom mold = 8 hours of exposure/day.
- Workplace mold = 8 hours of exposure/day.
- Car mold = ? hours of exposure/day.
A more toxic species will affect the body more quickly — but most folks live in mold for months or years before they realize something is amiss.
(3)
Your Health Status
A healthy body and mind will be more resilient to environmental toxicity.
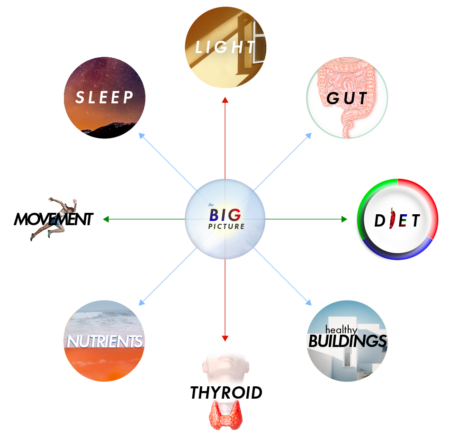
Gut health, light, sleep, nutrient balance, movement, and even your mindset are all critical factors in your overall health, and therefore, resilience to environmental toxins like mold.

People with a weakened immune system… are more likely to get mold infections.
US Center For Disease Control (CDC)
However, great health is not 100% protective. There are plenty of stories involving healthy folks falling victim to the effects of mold exposure — especially when a building is extremely moldy.
There is some evidence that certain genes can affect how much people are affected by mold. While this knowledge may provide some clues as to why mold is affecting you, it can easily serve as a distraction from the best steps forward. In other words, you don’t need a gene test to tell you a sick building is affecting you negatively.
(4)
The Species Growing
Some species release more mycotoxins, harmful VOCs (volatile organic chemicals), and spores than others.
Most Harmful Species
- Stachybotrys (this may be the worst of all)
- Cladosporium
- Chaetomiumspp
- Fusarium
- Aspergillus
Sometimes, worrying about the species of mold growing in your house can also serve as a distraction from what matters — controlling moisture, controlling humidity, contacting trusted remediators, or removing yourself from the exposure.
Mold Testing For Species
Proper mold lab tests identify mold species by their DNA.
Unfortunately, lab testing — while useful — can be limited and even costly. Many folks only use tests to avoid addressing mold. Others will be overwhelmed by the readings no matter their result.

Lab testing can be useful when trying to convince “higher ups” (landlords, legal entities, family members) who are skeptical of a problem.
Unfortunately, false negatives are possible with testing. Test multiple times if necessary, or use a different test that can more accurately demonstrate what’s happening.
Mold test kits sold at local stores (or online) aren’t scientific. Limitations and all, the only legitimate tests are ERMI and HERTSMI tests.
Related Articles

Why ‘Nobody’ Believes the Mold Sufferer
If there were a battle hymn of the mold sufferer, it would be titled: “Why Does Nobody Believe Me?”

An Exercise for Dealing With Loved Ones We Disagree With
An 11-question inventory for furthering relationships.

What I Do (New: 7-15-2023)
Here’s what I’m currently doing to improve my health.

‘Sensitization’ = Environmental Illness?
An introduction to environmental sensitivities.